What is the target material
The target material is the material used to make thin films. The target material is bombarded by high-speed charge carriers, and different film systems are obtained through the interaction of different lasers (ion beams) and different target materials, achieving conductivity and barrier functions
So the target material, also known as "sputtering target material", works by using ions generated by an ion source to gather and accelerate in vacuum. The high-speed ion beam formed is used to bombard the surface of the target material, undergo kinetic energy exchange, and allow atoms on the surface of the target material to deposit on the substrate
A target material is composed of a "target blank" and a "back plate", which is made of high-purity metal and is the target of high-speed ion beam bombardment. The back plate is connected to the target billet through welding process to fix the target billet, and the back plate needs to have conductivity and thermal conductivity
Thin Film Deposition
Thin film deposition is an essential link, which can be divided into PVD (Physical vapor deposition) and CVD (chemical vapor deposition). Generally speaking, it can be divided into physical deposition and chemical deposition
Physical deposition refers to the use of physical methods to convert a material source into gaseous particles and deposit them on a substrate under vacuum conditions. There are two common PVD methods: sputtering and evaporation. Sputtering mainly includes DC Physical vapor deposition, RF Physical vapor deposition, ionized Physical vapor deposition, and magnetron sputtering; Evaporation plating includes vacuum evaporation plating and electron beam evaporation plating
Chemical deposition refers to the method of generating thin films by chemical reactions of several vapor phase compounds or elemental substances containing thin film elements on the substrate surface. Common CVD methods include chemical vapor deposition and Atomic layer deposition. Chemical vapor deposition includes atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition, low-pressure chemical vapor deposition, metal chemical vapor deposition, photochemical vapor deposition, and laser chemical vapor deposition; Atomic layer deposition can be regarded as CVD chemical deposition in disguised form
Target Industry Chain
The target industry chain can be roughly divided into four links, namely metal purification, target manufacturing, sputtering coating, and terminal application. After extracting target materials from high-purity metals and using sputtering technology for coating, they are applied in fields such as chips, flat panel displays, solar cells, storage, optics, etc
In the four links of the target material industry chain, the strict technical requirements are metal purification and sputtering coating
Metal purification means to obtain more pure and regular main metal from irregular metal through chemical electrolysis, thermal decomposition or physical evaporative crystallization, Electromigration, vacuum melting and other methods
The existing metal purification capacity is generally concentrated in countries such as Japan and the United States, where the resources and production capacity of high-purity metals are more concentrated. Most domestic target material manufacturers rely on imports, and only a few high-purity metal materials can be self-sufficient
Target production is something that target manufacturers need to do, and downstream requirements for target purity are quite high. Generally speaking, solar cells and flat panel displays require a target material of 4N, while integrated circuit chips require a target material of 6N with higher purity
Sputtering is the responsibility of contract manufacturers, namely TSMC and Semiconductor Manufacturing International Corporation
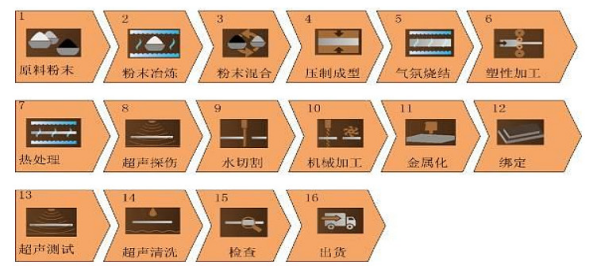
At present, domestic target manufacturers can be divided into two categories. One is responsible for internal metal purification. Raw materials start from metal powder, metal, non-metal, alloy, compound and other materials, and manufacturers can produce targets after their own purification; Another type is that the internal department is not responsible for metal purification. The raw materials start from the target billet, and the manufacturer is only responsible for welding, machining, testing, cleaning, and other work to produce the target material
The terminal applications of the target industry chain mainly fall into five categories, namely display panel target (LCD), semiconductor target, solar cell target (PV), magnetic recording target (mechanical keyboard), and energy-saving glass target. Among them, flat panel displays (28%), recording media (30%), and solar cells (27%) account for the majority, while semiconductor targets (9%) account for a smaller proportion




